DLSS: Enhancing Gaming Performance Explained
Nvidia's DLSS, or Deep Learning Super Sampling, stands as a pivotal innovation in the realm of PC gaming, revolutionizing performance and extending the life of graphics cards. Launched in 2019, DLSS has evolved through multiple iterations, enhancing its capabilities and differentiating features across Nvidia's RTX series. This guide will delve into what DLSS is, its mechanics, the differences between versions, and why it's significant—even for those not currently using Nvidia graphics cards.
Additional contributions by Matthew S. Smith.
What Is DLSS?
Nvidia DLSS, short for Deep Learning Super Sampling, is a proprietary system designed to boost both the performance and visual quality of games. The "Super Sampling" aspect refers to its ability to upscale games to higher resolutions using a neural network trained on extensive gameplay data. This method allows for higher resolutions with minimal performance impact compared to manually setting a higher resolution in-game.
Beyond its initial upscaling function, DLSS now encompasses several systems that enhance image quality. These include DLSS Ray Reconstruction, which improves lighting and shadow quality using AI; DLSS Frame Generation and Multi Frame Generation, which use AI to insert additional frames to boost FPS; and DLAA (Deep Learning Anti-Aliasing), which enhances graphics beyond native resolution capabilities.
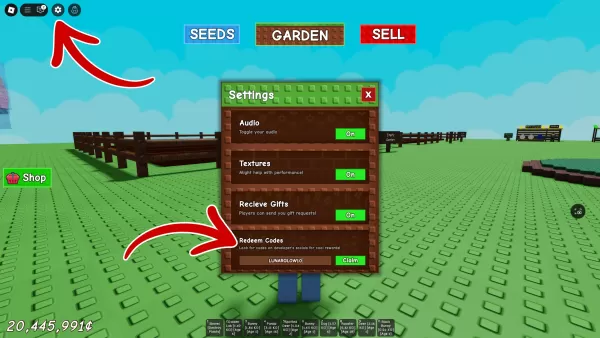
Super Resolution, the most recognized feature of DLSS, is particularly beneficial when paired with ray tracing. In supported games, you can enable DLSS through various modes such as Ultra Performance, Performance, Balanced, and Quality. For instance, in Cyberpunk 2077, selecting 4K resolution with DLSS Quality mode means the game renders at 1440p, which DLSS then upscales to 4K, resulting in significantly higher frame rates due to the lower rendering resolution and AI-driven upscaling.
DLSS's neural rendering differs from older techniques like checkerboard rendering, adding details not visible at native resolution and preserving details lost in other upscaling methods. However, it can introduce artifacts like "bubbling" shadows or flickering lines, though these have been significantly reduced with DLSS 4.
The Generational Leap: DLSS 3 to DLSS 4
With the RTX 50-series, Nvidia introduced DLSS 4, which overhauls the AI model to enhance quality and capabilities. DLSS 3, including DLSS 3.5 with frame generation, utilized a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) trained on vast video game datasets. However, DLSS 4 shifts to a Transformer model, or TNN, capable of analyzing twice as many parameters for a deeper scene understanding. This model interprets inputs more sophisticatedly, including long-range patterns, leading to sharper gameplay and reduced artifacts.
DLSS 4's TNN model significantly improves Super Sampling and Ray Reconstruction, retaining finer details and reducing visual anomalies. Additionally, DLSS Multi Frame Generation can now generate four artificial frames for each rendered frame, dramatically increasing frame rates. To mitigate concerns about input lag, Nvidia integrates Nvidia Reflex 2.0, which reduces latency to maintain responsiveness.
While DLSS Multi Frame Generation is exclusive to the RTX 50-series, the new Transformer model's image quality benefits are available to all RTX users via the Nvidia App, which also allows enabling DLSS Ultra Performance mode and DLAA in unsupported games.
Why Does DLSS Matter for Gaming?
DLSS is a game-changer for PC gaming, particularly for users with mid-range or lower-performance Nvidia graphics cards. It enables higher graphics settings and resolutions, extending the life of your GPU. As graphics card prices continue to rise, DLSS offers a cost-effective way to maintain playable frame rates by adjusting settings or performance modes.
DLSS has also spurred competition, with AMD and Intel introducing their own upscaling technologies, AMD FidelityFX Super Resolution (FSR) and Intel Xe Super Sampling (XeSS). While Nvidia's DLSS leads in image quality and frame generation capabilities, the competition has lowered the price-to-performance barrier in many gaming scenarios.
Nvidia DLSS vs. AMD FSR vs. Intel XeSS
Nvidia's DLSS faces competition from AMD's FidelityFX Super Resolution (FSR) and Intel's Xe Super Sampling (XeSS). DLSS 4's superior image quality and multi-frame generation capabilities give it an edge, though all three technologies offer intelligent upscaling and frame generation. DLSS generally provides a crisper, more consistent image with fewer artifacts.
However, DLSS is exclusive to Nvidia graphics cards and requires game developer implementation, unlike AMD FSR. While many games now support DLSS, FSR, and XeSS, availability can vary, and there's no default enablement option for DLSS.
Conclusion
Nvidia DLSS has transformed the gaming industry, continually improving and showing no signs of slowing down. It significantly enhances gaming experiences and extends GPU longevity. While AMD and Intel have introduced competing technologies, choosing the right GPU involves balancing cost, features, and game compatibility to find the best value for your gaming needs.
-
Earlier this year, Niantic, the developer of Pokémon Go, announced the sale of its mobile game portfolio to Scopely, the company behind Monopoly Go, in a $3.5 billion deal. This development was met with both enthusiasm and criticism from the game's dAuthor : Benjamin Nov 15,2025
-
Warner Bros. and New Line Cinema have revealed the premiere date for The Lord of the Rings: The Hunt for Gollum, with the Sméagol-centric story hitting theaters on December 17, 2027.The newly announced release pushes the film over two years beyond thAuthor : Eleanor Nov 15,2025
- Black Ops 6 Zombies: How To Configure The Summoning Circle Rings on Citadelle Des Morts
- Harvest Moon: Lost Valley DLC and Preorder Details Revealed
- Roblox: Latest DOORS Codes Released!
- Silent Hill 2 Remake Coming to Xbox and Switch in 2025
- Roblox: Blox Fruits Codes (January 2025)
- Roblox: Freeze for UGC Codes (January 2025)

















![Taffy Tales [v1.07.3a]](https://imgs.ehr99.com/uploads/32/1719554710667e529623764.jpg)